Abstract
Introduction:
Management of Hemophilia A and B require intravenous factor VIII (FVIII) and factor IX (FIX) infusions respectively to replenish missing coagulation factor. We compared real world expenditures in the US for clotting factor concentrates associated with treatment of Hemophilia A and B patients with EHL products versus recombinant standard half-life (SHL) products.
Methods:
De-identified claims data from the Truven Health MarketScan® Research US claims databases were used to identify male patients with either hemophilia A who received FVIII replacement from August, 2014 (month first EHL FVIII product dispensed) to April 2017; or hemophilia B who received FIX replacement from June 2014 (month first EHL FIX product dispensed) to April 2017 and had data for at least 3 months of dispensation. The two groups of patients (SHL vs EHL) were compared. Key outcome measures were direct expenditures and factor IUs dispensed for factor replacement products. Expenditures and IUs dispensed were measured over quarterly (3-month) increments for 10 quarters in each group (SHL & EHL). Descriptive statistics were used to analyze results. Medians for expenditures and IUs were used to accommodate for the skewness of data distribution.
Results:
Hemophilia A
538 Hemophilia A patients were included in the analysis (437 SHL; 104 EHL), including patients who switched from one class to the other. Quarterly expenditures and IUs dispensed were analyzed for these patients up to 30 months.
The median quarterly study period factor per patient expenditure was $72,466 higher (2.15 times) in the EHL cohort ($135,392; IQR: $101,690-$189,501) compared with the SHL cohort ($62,927; IQR: $19,448-$121,192). Median quarterly study period per patient IU dispensation was also higher in the EHL cohort (68,736 IUs; IQR: 49,687-100,883) vs SHL users (48,473 IUs; IQR: 13,396-91,102).
Median total Hemophilia A related expenditures were $137,210 and $66,713 in the EHL and SHL cohorts indicating that the total expenditures were chiefly due to factor replacement.
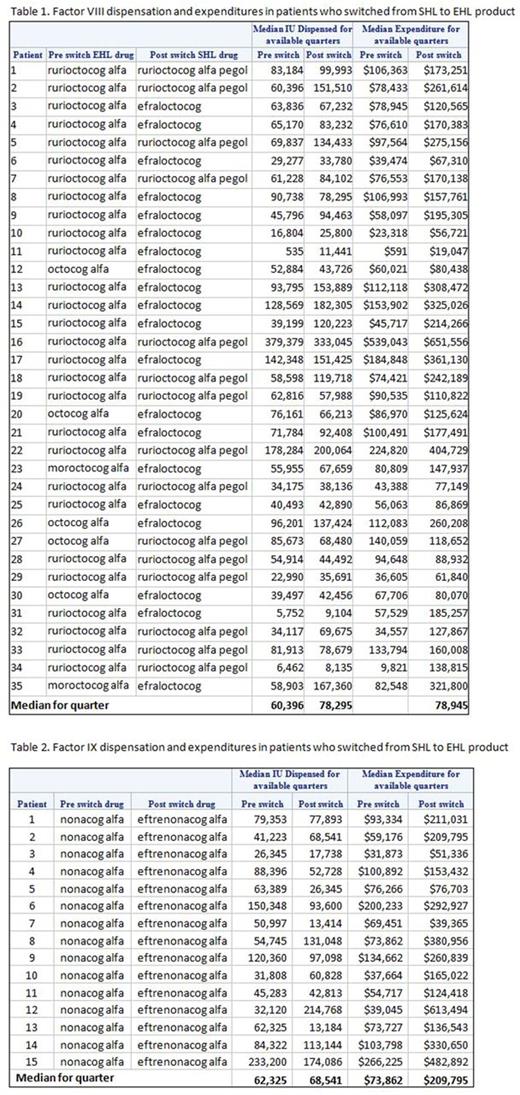
In the switch analysis, 35 patients had switched from one of three SHL FVIII products to one of two EHL FVIII products. The total median IU dispensation per calendar quarter increased following the switch from 60,396 IU (pre-switch, SHL) to 78,295 IU (post-switch, EHL; 30% increase), as did the factor-related expenditure ($78,945, SHL, versus $160,008, EHL; 103% increase).
Hemophilia B
104 Hemophilia B patients that had at least 3 months data were included in the analysis (79 SHL; 25 EHL). Quarterly expenditures and IUs dispensed were analyzed for these patients over up to 30 months.
The median quarterly study period factor per patient expenditure was $106,441 higher (2.8 times) in the EHL cohort ($165,022; IQR: $97,444-$260,839) compared with the SHL cohort ($58,580; IQR: $26,864 - $113,959). Median quarterly study period per patient metric IU dispensation was also higher in the EHL cohort (68,541 IUs; IQR: 33,941-97,098) vs SHL users (39,180 IUs; IQR: 19,000-87,550).
Median total Hemophilia B related expenditures were $165,188 and $60,713 in the EHL and SHL cohorts indicating that the total expenditures were chiefly due to factor replacement.
In the switch analysis, 15 patients with hemophilia B switched from SHL to EHL. Median quarterly per-patient factor expenditure for up to 30 months pre/post-switch was $73,862 (IQR: $54,717-$103,798) in the period pre-switch, and $209,795 (IQR: $124,418-$330,650) after the switch. Median quarterly per-patient metric IUs utilization pre-switch was 62,325 (IQR: 41,223-88,396) and 68,541 (IQR: 26,345-113,144) IUs post-switch.
Conclusion:
This real-world data analysis, unadjusted for treatment regimen or disease severity, showed a higher expenditure associated with EHL use in both Hemophilia A and Hemophilia B treatment in the US. Median quarterly study period per patient IU dispensation was also higher in the EHL cohort for both Hemophilia A and B. These real-world data may challenge assumptions regarding typical factor usage and expenditures associated with EHL products in patients with hemophilia A and B. Further analyses, incorporating essential clinical characteristics, should be explored.
Chhabra: Pfizer Inc: Employment, Other: Stockholder. Alvir: Pfizer Inc: Employment, Other: Stockholder. Spurden: Pfizer Limited: Employment, Other: Stockholder. Fogarty: Pfizer Inc: Employment, Other: Stockholder. Tortella: Pfizer Inc: Employment, Other: Stockholder. McDonald: Pfizer Inc: Employment, Other: Stockholder. Pleil: Pfizer: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.